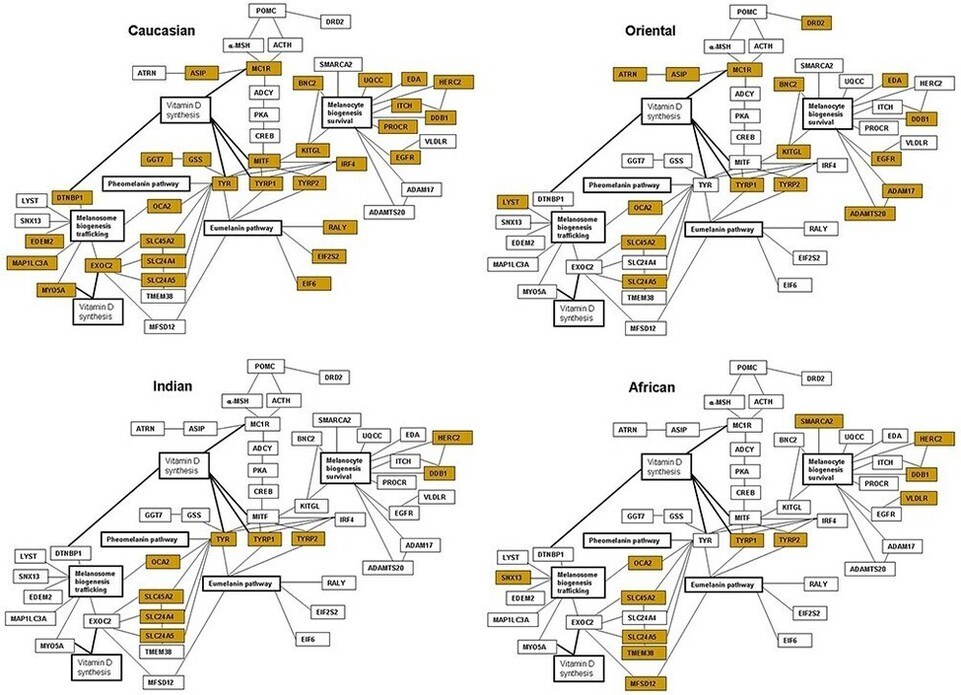
SINGLE NUCLEOTIDE POLYMORPHISM (SNP) DATABASE
SNP-based DNA analysis offers a unique and completely novel approach to personalised skincare. This would involve a relatively straightforward collection of swab samples and rapid sequencing for the subsequent comparison with the information in the database. Assembly of the personal profile would highlight the specific requirements for the uniquely tailored topical product to enhance the individual characteristics and ameliorate the undesirable problems.
We have established an extensive database of thousands of SNPs that are detected within the pool of genes responsible for skin phenotypes and function. This captured information on the genes allows for creation of eight characteristics highlighting the unique cosmetic requirements for each skin type alongside the established or predicted effects of the SNPs. One of the crucial benefits of the SNP-based analysis is that it
would allow distinguishing between the cause and the effect of a particular problem. For example, inflammation is associated with both sunburns and xerosis, SNP profile could help to establish if the inflammation is the result of these problems or the factor driving them, for example leading to much more sensitive skin.